What is Diabetic Retinopathy?
Diabetic retinopathy is an eye disease that can be present in people with diabetes. It is when high blood sugar levels have damaged the blood vessels in the retina.
The disease can cause the blood vessels to swell and leak, or they can close, stopping blood from passing through. Sometimes abnormal new blood vessels can grow on the retina. All of these can cause vision loss.
- Seeing an increasing number of floaters
- Blurry vision or vision going from blurry to clear
- Losing vision
- Having poor night vision
- Noticing colors appear faded or washed out
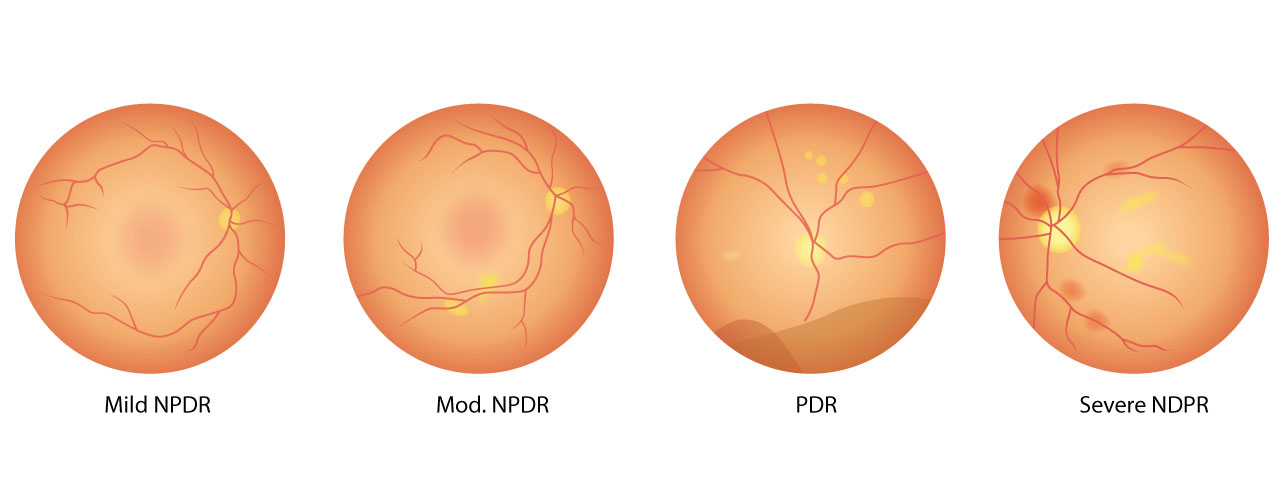
Stages of diabetic eye disease
- NDPR: NDPR (non-proliferative diabetic retinopathy) is the early stage of diabetic eye disease. NDPR can result in macular edema, where the blood vessels leak and result in the macula swelling, while macular ischemia is when the blood vessels in the retina begin to close off. Both of these conditions can result in blurry vision.
- PDR: PDR (proliferative diabetic retinopathy) is the more advanced stage of diabetic eye disease. This happens when the retina begins to grow new blood vessels. These fragile vessels can cause new floaters or block all vision due to bleeding. It can also form scar tissue which can cause a detached retina or problems with the macula. It's a very serious condition that can steal central and side vision.
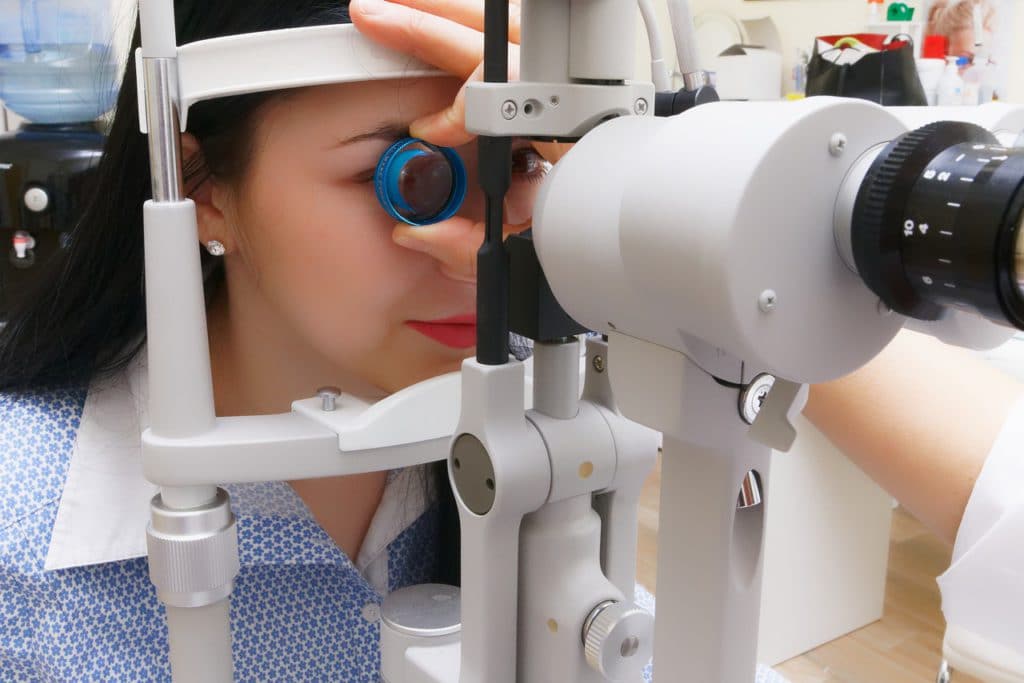
Drops will be put into your eye to dilate your pupil. The ophthalmologist will look into your eye with a special lens.
- Fluorescein angiography: Yellow dye is injected into a vein and travels through your body. A special camera is then used to take photos of the veins, seeing if there is any blockage or leaking. It also shows if there are abnormal veins loading.
- Optical coherence tomography (OCT): A machine is used to scan the retina and provides detailed images of its thickness. This helps the doctor find and measure the swelling of your macula.
How is it treated?
- Medical control: Controlling your blood sugar and blood pressure can stop vision loss. Follow a diet and take the prescribed medication recomended by your doctor. This will keep your eyes healthy and may even help in recovering some lost vision.
- Medicine: One type of medication used is called "anti-VEGF" medication, which is given by shots in the eye. It helps to reduce swelling of the macula, slowing vision loss and may improve vision. Steroid medication is another choice to reduce swelling and also given as shots. Your doctor will recomend how many injections you will need over time
- Laser Surgery: This would be used to seal off leaking blood vessels. It can also be used to shrink blood vessels and stop new ones from growing. It can help to reduce swelling in the retina. Multiple treatments may be required
- Vitrectomy: If the PDR is advanced, the ophthalmologist may reccomend this treatment. The opthalmologist would remove vitreous gel and blood from leaking vessels in the back of your eye. This results in light rays able to focus on the retina again. It can also be done to remove scar tissue.
It is important to get treated as soon as possible for diabetic retinopathy as soon as possible to prevent vision loss. Regular diabetic eye checkups are recomended and may even catch it before any vision problems appear.